
Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC)
The triangular fibrocartilaginous complex (TFCC) is a highly unique and complex structure with several parts, including the distal radio-ulnar joint (DRUJ), and that fills the space between the ulnar and carpal (ulnocarpal).
The TFCC is made up of several parts:
- the discus (intervertebral disc of the hand)
- radius and ulna attachments
- the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) ligaments
- the ulnocarpal ligaments
- and the tendon sheath of the ulnar collateral ligament
The function of the TFCC is to:
- Stabilize and guide rotational DRUJ movements
- Stabilize and guide the ulnocarpal joint
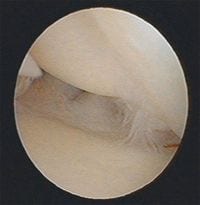
Hands can be injured by a fall, for example, and certain parts can also become frayed and worn down by use.
Radial fractures of the TFCC are often overlooked (see section on radial fractures) and can cause persistent pain long after the fracture has healed. In cases where pain persists even after the fracture has healed, it is very important to clarify the causes.
In addition to a range of conservative therapies (splints, tape dressing, ergotherapy, etc.), it is sometimes necessary to carry out an operation, for example, if fissures are developing and the pain and discomfort are great.
For an operation of this kind, arthroscopy (the keyhole technique) is clearly the method of choice. Prior to surgery, however, the extent of the injury needs to be clarified with an MRI, in particular to evaluate whether an operation really is the best path.
ARTHROSCOPY
Arthroscopy of the wrist can be carried out under local (plexus anesthesia) or general anesthesia at the patient's request. The operation itself is generally not a significant burden as there is no blood loss for the body to cope with. However, the patient must be fully aware of all possible complications (mainly possibly injury to tendons and nerves).

The majority of indications for arthroscopy of the wrist involve the articular disc complex in the wrist. Other causes are ligament injuries and loose fragments. All these complications can also lead to an irritation of the synovial membrane (synovitis), which can cause pain and restrict mobility.
In the case of an articular disc injury, the disc is sutured, smoothed, or even partially removed, depending on the type of tear. Only the unstable part of the torn articular disc must be removed, however, the edge with the ligament attachments must always be retained.
More questions?
Our experts are happy to help you
Just give us a call!




